Automation is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a daily reality for organizations of every size. Two of the most talked-about technologies in this space are robotic process automation and artificial intelligence. They are often mentioned together, compared side by side, and sometimes even confused with each other.
In this guide, we explore RPA vs AI in simple, business-friendly terms and explain the differences between the two. You will also learn what is a virtual agent, and understand the role of AI in modern contact centers, showing how these technologies can work together to drive efficiency, innovation, and growth.
Beyond contact centers, AI is transforming the way businesses leverage cloud computing with AI, allowing data and applications to scale seamlessly while reducing infrastructure costs. Computer technology, AI-driven solutions are improving processing power, predictive analytics, and decision-making capabilities, enabling smarter operations across industries.
Businesses are also tapping into marketing with AI, using intelligent algorithms to understand customer behavior, personalize campaigns, and optimize outcomes. Digital marketing using AI is now a staple for brands that want to deliver targeted content, enhance engagement, and increase conversions with precision.
In finance, financial AI is revolutionizing risk assessment, fraud detection, and investment strategies, making operations faster, more accurate, and highly secure. When combined with RPA, these AI-powered solutions create a seamless workflow that handles repetitive tasks while providing deep insights for strategic growth.
By understanding RPA vs AI and its applications across cloud computing, technology, marketing, and finance, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation that were previously unimaginable.
Top AI Contact Center Solutions to Understand RPA vs AI
When exploring RPA vs AI, it’s crucial to see how these technologies are applied in real-world contact center solutions. AI-powered platforms not only automate repetitive tasks but also enhance customer engagement, improve agent productivity, and provide actionable insights. Here are the top solutions leading the way:
1. Bright Pattern: Leading AI Contact Center Solution for RPA vs AI Integration
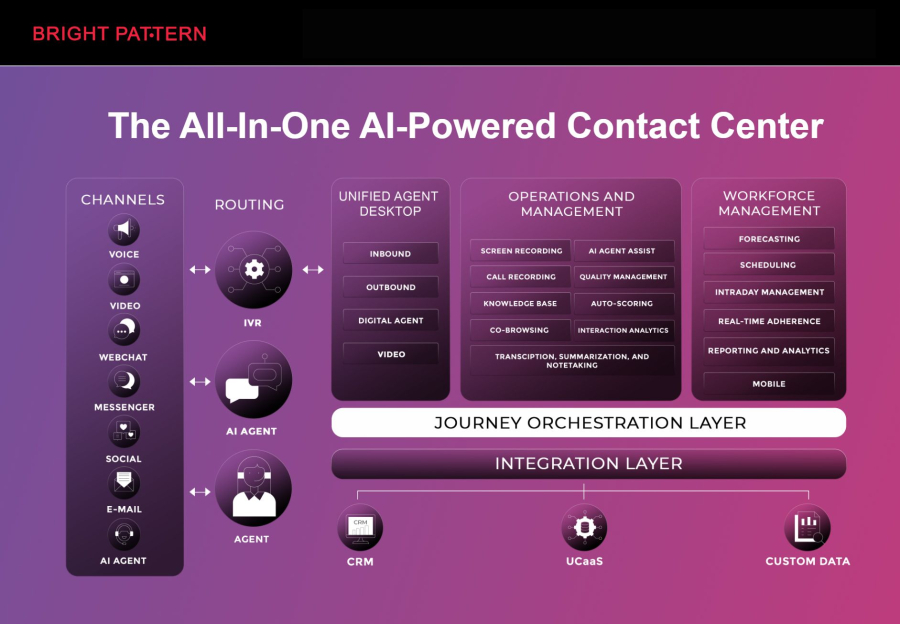
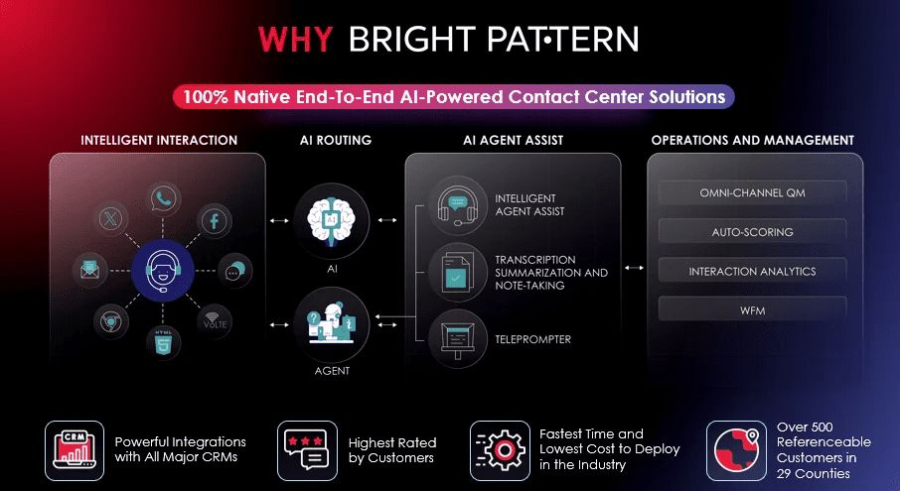
Bright Pattern is a cloud-based AI contact center platform designed to streamline communication across channels while integrating AI and RPA capabilities. By combining virtual agents, predictive routing, and AI analytics, Bright Pattern helps organizations deliver smarter, faster, and more personalized customer service.
Key features include:
- Omnichannel support: Voice, chat, SMS, email, and social media interactions unified in one platform.
- AI-powered virtual agents: Handle routine inquiries, escalate complex issues to live agents, and provide consistent responses.
- RPA integration: Automate repetitive back-office tasks like data entry, order updates, and CRM updates.
- Advanced analytics: Real-time dashboards track agent performance, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
- Scalability in the cloud: Quickly scale operations without heavy infrastructure investment.
Bright Pattern is particularly useful for organizations aiming to combine RPA with AI to improve both efficiency and customer satisfaction, making it a top choice for modern contact centers.
2. Genesys Cloud CX
A powerful platform that blends AI-driven insights with RPA tools to enhance customer engagement and agent productivity.
3. Five9 Intelligent Cloud Contact Center
Offers AI chatbots, predictive dialing, and workflow automation to optimize customer interactions.
4. NICE inContact CXone
Integrates RPA with AI-powered analytics to improve agent performance and automate routine processes.
5. Talkdesk CX Cloud
Provides AI-driven virtual agents and automation tools for efficient contact center operations.
6. Avaya OneCloud CCaaS
Combines AI, RPA, and omnichannel capabilities for seamless customer experience management.
7. Cisco Webex Contact Center
Uses AI virtual agents, analytics, and automated workflows to improve resolution times.
8. RingCentral Contact Center
Focuses on AI-enabled routing and workflow automation to reduce wait times and enhance engagement.
9. HubSpot Service Hub
Offers AI chatbots and automation features to streamline customer service and support workflows.
10. Zoho Desk
Combines AI, automation, and cloud-based management to optimize ticketing and support efficiency.
Quick Snapshot: RPA vs AI
Before diving into the details, here is a high level view:
- RPAautomatesrule based, repetitive tasksby mimicking human actions on computers and systems.
- AIaims to replicate aspects ofhuman intelligencesuch as learning, reasoning, perception, and decision making.
- RPAis usually faster to implement and easier to govern, offering quick wins and strong ROI on routine processes.
- AIshines in dealing withcomplex, variable, and unstructuredproblems where rules alone are not enough.
- The biggest opportunity lies in combining them intointelligent automationthat is both fast and smart.
What Is RPA (Robotic Process Automation)?
Robotic process automationuses software robots, or "bots," to perform structured, repetitive tasks across digital systems. These bots follow defined rules and interact with applications just like a human would: clicking, typing, copying, pasting, and moving data between systems.
Typical RPA characteristics
- Rule based: Bots follow explicit instructions and workflows defined by humans.
- Deterministic outcomes: For the same input and rules, RPA produces the same result every time.
- Works best with structured data: Spreadsheets, forms, databases, and standardized digital inputs.
- UI level interaction: Bots often work through the user interface, replicating mouse clicks and keyboard entries.
- Non invasive: Usually does not require deep changes to underlying systems or infrastructure.
Common RPA use cases
- Invoice processing: Extracting data from standardized invoices and entering it into accounting systems.
- Employee onboarding: Creating user accounts, assigning system access, and sending standardized welcome messages.
- Order entry: Transferring data from email or order forms into CRM or ERP systems.
- Report generation: Pulling data from multiple systems, consolidating it, and producing regular reports.
- Data migration: Moving records between legacy and modern applications.
The core benefit of RPA isspeed and accuracy on repeatable tasks. It reduces manual effort, eliminates many human errors, and frees employees to focus on higher value work.
What Is AI (Artificial Intelligence)?
Artificial intelligenceis a broad field focused on building systems that can perform tasks which normally require human intelligence. These tasks include understanding language, recognizing patterns, making predictions, and learning from experience.
Many AI systems today rely onmachine learning, where models learn from data instead of being explicitly programmed with every rule. As they are exposed to more data, they can improve their performance or adapt to new patterns.
Typical AI characteristics
- Data driven: Learns from large volumes of data rather than fixed rule sets alone.
- Probabilistic outcomes: Provides predictions or classifications with varying degrees of confidence.
- Handles unstructured data: Text, images, audio, and other complex inputs.
- Adaptive: Can improve over time as new data and feedback are incorporated.
- Cognitive capabilities: Encompasses perception, language understanding, prediction, and reasoning.
Common AI use cases
- Document understanding: Extracting key information from varied contracts, claims, or forms.
- Customer service assistants: Conversational agents that can understand questions and provide relevant responses.
- Predictive analytics: Forecasting demand, churn risk, or equipment failures.
- Image and pattern recognition: Identifying objects in images or spotting anomalies in sensor data.
- Personalized recommendations: Suggesting products, content, or next best actions for users.
The key strength of AI is its ability tomake sense of complexity. Where RPA follows pre set rules, AI can interpret messy data, detect patterns, and support smarter decisions.
RPA vs AI: Key Differences at a Glance
RPA and AI both automate work, but they approach it in different ways. The table below highlights their main differences and unique benefits.
|
Aspect |
RPA |
AI |
|
Primary focus |
Automating repetitive, rule based tasks |
Replicating aspects of human intelligence and judgment |
|
Type of work |
Structured, predictable, high volume |
Complex, variable, often unstructured |
|
How it works |
Follows predefined rules and workflows |
Learns patterns from data and experience |
|
Data requirements |
Structured data, clear inputs and outputs |
Structured and unstructured data, large datasets |
|
Outcome type |
Deterministic: same input, same output |
Probabilistic: best guess with a confidence level |
|
Implementation speed |
Often faster to deploy within existing systems |
May require more time for data, modeling, and tuning |
|
Ideal benefits |
Efficiency, accuracy, cost savings on routine work |
Smarter decisions, insights, and personalized experiences |
|
Best suited for |
Stable, rule based processes with little variation |
Scenarios where rules are unclear or data is complex |
Where RPA Shines
If your goal is toreduce manual effort quicklyin processes that follow clear rules, RPA is extremely effective. Some standout advantages include:
- Fast time to value: Many RPA projects can be piloted and scaled in weeks rather than months.
- High accuracy: Once configured, bots do not get distracted or fatigued, leading to fewer errors.
- Cost efficiency: Routine workloads can be handled at scale without continuously expanding headcount.
- Better compliance: Every action of a bot can be logged, making audits and traceability easier.
- Employee experience: Staff are freed from monotonous tasks and can focus on work that requires human empathy and creativity.
RPA is particularly powerful for organizations with many legacy systems that do not easily integrate. Bots can bridge gaps by moving data between systems without major infrastructure changes.
Where AI Shines
AI becomes especially valuable when your processes involveambiguity, judgment, or large amounts of datathat are hard to handle with simple rules. Its benefits include:
- Deeper insights: Detects patterns and relationships that are not obvious to humans.
- Better decisions at scale: Provides recommendations or risk scores for thousands or millions of cases.
- Personalization: Tailors content, offers, and interactions to individual users or segments.
- Handling unstructured content: Interprets text documents, images, or other non tabular data sources.
- Continuous improvement: Models can be updated as conditions change, keeping decisions aligned with reality.
AI is ideal when you want your systems not just todotasks, but tounderstand, analyze, and optimizehow those tasks are performed.
RPA vs AI: Common Misconceptions
Because both technologies relate to automation, several myths tend to surface. Clarifying these helps you design better solutions.
Myth 1: RPA is a form of AI
On its own,RPA is not AI. It is a rule based automation technology. While both can work together, RPA by itself does not learn or adapt; it executes instructions defined by humans.
Myth 2: AI will automatically replace RPA
AI does not eliminate the need for RPA. In fact, most successful automation programs useboth technologies. RPA handles structured workflows, while AI enhances those workflows with smarter decision points.
Myth 3: AI can be dropped into any process instantly
AI is powerful, but it relies ondata quality, clear objectives, and proper governance. It typically requires more preparation and iteration than RPA. When implemented thoughtfully, the results can be transformative, but it is not a plug and play solution for every scenario.
When to Choose RPA, AI, or Both
The right choice depends on your process, your data, and your goals. Use the guide below to align technology with value.
Choose RPA when:
- The process isstable and well defined.
- Inputs and outputs arestandardized and structured.
- There areclear rules and decision treesthat rarely change.
- You needquick efficiency winsand rapid ROI.
- Your systems are diverse or legacy, and integration options are limited.
Choose AI when:
- You facecomplex decisionsthat are hard to encode as fixed rules.
- You want to leveragelarge datasetsto gain insights or predictions.
- Your inputs includetext, images, or free form content.
- Personalization, forecasting, or anomaly detection are high priorities.
- You are prepared to invest indata, experimentation, and model lifecycle management.
Choose both (intelligent automation) when:
- You wantend to end automationthat covers data capture, understanding, decisioning, and execution.
- Your process hasrepeatable stepsbut alsojudgment callsalong the way.
- You aim to deliver24/7, high quality servicewith minimal manual intervention.
In many cases, a blended approach offers the best of both worlds: RPA executes tasks consistently, while AI powers the intelligence behind those tasks.
How RPA and AI Work Together
When combined, RPA and AI createintelligent automation. This is where organizations often see the most dramatic impact, moving beyond isolated task automation to smarter, adaptive workflows.
Example 1: Intelligent document processing
Imagine a process where your team receives thousands of varied documents each week: contracts, claims, applications, or onboarding forms.
- AI modelsread and interpret the documents, extracting key data fields and understanding document types and intent.
- RPA botstake that structured output and enter it into core systems, update records, and trigger downstream workflows.
The result is a highly automated pipeline that can handle different layouts, formats, and content styles, while still integrating seamlessly with existing systems.
Example 2: Smarter customer service
Consider a support environment where customers contact you through chat or email.
- AI powered language modelsclassify incoming messages, detect intent, and suggest responses.
- If the query is routine and low risk, anRPA botcan process the request end to end: updating records, issuing confirmations, and closing the ticket.
- For more complex issues, AI supports human agents with recommended actions, while RPA handles the repetitive steps so agents can focus on the relationship.
This combination shortens response times, maintains consistency, and allows your team to focus on high impact interactions.
Example 3: Risk and compliance automation
In finance, healthcare, and other regulated sectors, compliance checks are critical but often labor intensive.
- AI modelscan flag unusual patterns, potential anomalies, or higher risk cases based on historical data.
- RPA botsthen perform standardized checks, gather evidence, and generate audit ready reports.
The combination enhances bothcoverageandconsistency, reducing risk while minimizing manual workload.
Designing a Winning Automation Strategy
Whether you lean towards RPA, AI, or a blend of both, a strategic approach helps you maximize outcomes and avoid scattered initiatives.
1. Start with business goals, not technology
Clarify what you want to achieve: cost reduction, faster cycle times, better customer satisfaction, higher accuracy, or all of the above. Map these goals to specific processes and metrics so you can measure impact.
2. Build a prioritized automation pipeline
Identify and rank candidate processes based on:
- Volume: How often is the process executed?
- Effort: How much manual time does it consume?
- Stability: Are the steps and rules relatively consistent?
- Data complexity: Are inputs structured, semi structured, or unstructured?
- Business impact: What is the potential value of improving this process?
Processes withhigh volume, high effort, and clear rulesare ideal RPA starting points. As you move to more complex or unstructured scenarios, AI and intelligent automation come into play.
3. Invest in process and data understanding
For RPA, detailed process mapping avoids rework and ensures bots align with real world workflows. For AI, strong data foundations support reliable models. Document exceptions, decision points, and data sources early in your journey.
4. Combine human and digital strengths
Automation is most effective when it enhances people, not replaces them. A balanced model often looks like this:
- Botshandle repetitive, structured execution.
- AIprovides insights, triage, and recommendations.
- Humansreview edge cases, handle complex exceptions, and maintain customer relationships.
This approach protects quality, supports adoption, and positions your workforce to focus on strategic, creative, and interpersonal work.
5. Plan for governance and continuous improvement
As automation scales, it becomes a core part of how your business operates. Strong governance keeps it effective and trustworthy.
- Set clearownershipfor RPA bots, AI models, and underlying processes.
- Monitorperformance metricsand adjust workflows to capture new opportunities.
- Reviewmodel behaviorover time to ensure fairness, accuracy, and alignment with regulations.
- Encourage a culture ofexperimentation and feedbackso teams can propose new automation ideas.
The Bottom Line: RPA vs AI Is Not Either / Or
It is tempting to viewRPA vs AIas a competition. In reality, they are complementary tools in the same toolkit.
- RPAgives you speed, precision, and scalability for repetitive digital tasks.
- AIgives you intelligence, adaptability, and deeper insight into complex problems.
- Together, they allow you to buildintelligent automationthat elevates both operational efficiency and customer experience.
By understanding the strengths of each and aligning them with your business priorities, you can design automation initiatives that deliver measurable value, empower your teams, and keep your organization a step ahead in an increasingly digital world.
